航空航天技术是高度综合的现代科学技术,也是国家最高工业水平的体现之一。航空航天器在运行过程中需克服重力,且在高温、高速等复杂环境中服役,因此,该领域部件的轻质化要求非常高。钛合金具有高比强度、低密度的优点,可在室温到中高温环境服役,是航空航天零件应用的重要材料[1–2]。飞机 / 直升机的各类框、梁、机翼壁板、桨毂等[3],现役航空发动机的风扇 / 压气机转定子、压气机机匣、中介机匣等[4–5],航天用容器[6]、承力结构、紧固件[7]等采用钛合金材料制造,可谓应用广泛。与此同时,相比结构钢或镍基高温合金,钛合金也存在硬度低、耐磨性差、高温氧化抗力差等问题,表面应力集中敏感导致的机械疲劳问题(后简称疲劳)也较突出。综合来说,航空航天领域的钛合金零件长寿命高可靠服役需要克服 3 大问题——磨损、腐蚀和疲劳。
3大问题均为表面工程问题。为此,基于钛合金材料,国内外学术与工业领域开展了大量表面工程技术的基础和应用研究,目的是提高钛合金材料及零件的耐磨性、抗氧化性和疲劳抗力,最终实现涂层在钛合金零件的可靠应用。以下将分节对 3大类航空航天钛合金表面工程技术研究进展进行逐一探讨。实际上,钛合金还具备良好的生物相容性,被应用于医学植入物,这方面表面工程技术研究不在本研究讨论之列。特殊地,航空发动机钛合金叶片 / 机匣定转子摩擦部位还可能涂覆封严涂层,以保证气流密闭性提高气动效率,这是发动机单一部位的使用需求,本研究不专门论述。
1 、钛合金耐磨损涂层
钛合金硬度低、耐磨性较差是工业界共识,然而,为轻量化和耐室温腐蚀的需求,钛合金零件较多地应用于可能发生摩擦磨损的环境下,比较典型的应用为钛合金起落架活塞杆[8]。工业界采用各种手段将硬质涂层镀覆在钛合金表面,形成“硬壳软芯”结构,同时满足耐磨和受载的需求。
1.1 沉积、喷涂涂层
采用物理方法在较软的钛合金表面制备硬质涂层,是国内外工程界公认的耐磨方法。Hong 等[9] 利用电火花沉积技术在钛合金 TC11 表面镀覆 TiN 涂层,通过厚度、TiN 含量和空隙率等分析了工艺参数对涂层微观结构和耐磨性的影响,获得了优化沉积工艺和涂层磨损失效机制。
在 TC4 基体表面,曹鑫等[10] 采用物理气相沉积的方法制备了 TiN/Ti 梯度涂层,分析了梯度涂层结构在沙尘冲蚀损伤的影响,发现 TiN∶Ti=1∶3时,实现强韧性匹配,耐冲蚀性能最佳。Richard 等[11] 利用热喷涂法在钛合金表面制备 ZrO2–Al2O3–TiO2 纳米陶瓷涂层,该涂层相比单一 ZrO2 涂层具有更佳的摩擦系数、耐磨性和耐蚀性。在VT6钛合金表面,Koshuro等[12]采用等离子喷涂氧化铝结合后续微弧氧化方法制备金属氧化物涂层,硬度 提 高 到 1640HV。Liu 等[13] 利 用爆炸喷涂方法在 Ti–Al–Zr 合金表面制备了 HV1800 (压头载荷 5g)WC–Co 涂层,在 25~400℃的较宽温域提高 了 微 动 疲 劳 性 能。Pawlak 等[14]利用反应电弧沉积制备 Ti–C–N 底层后利用磁控溅射制备 WC–C 面层,使得 TC4 钛合金耐磨性提高 94%。
王俊等[15] 采用等离子喷涂在钛合金表面制备氧化物涂层,接着采用激光熔覆方法提高了氧化物涂层硬度。部分涂层结构如图 1 所示[9,11,14]。

1.2 激光熔覆涂层
预涂粉末混合干燥后进行激光熔覆的方法在钛合金表面产生硬质耐磨涂层,同样是国内外研究的热点。Mohazzab[16] 和 Wu[17] 等采用激光表面处理方法在纯钛或钛合金表面制备了 TiC 和 Ti–Si 硬质层,硬度可达到 1000HV0.1 以上,以提高硬度和耐磨性。Wang 等[18] 在 TC4 合金表面制备了耐磨性能更佳的精细片层结构纯钛涂层,认为激光熔覆过程的细晶强化作用是提高耐磨性的主要原因。高霁[19]、Zhao[20]、戈晓岚[21]、蒋松林[22]、李春燕[23]、林沛玲[24]、刘丹[25] 和刘庆辉[26] 等分别在钛合金表面制备CBN、Ti–O–N、Ti–Al–Nb、WC–Co、Ti–Si–C、Ti–B 或多元素复合(如掺Ni)硬质耐磨层,以引入更高的显微硬度和摩擦磨损性能。Ye[27]、任佳[28]和相占凤[29] 等在粉末中分别加入碳纳米管和 h–BN(六方氮化硼),在涂层中形成了软硬混合的相结构,起到了良好的耐磨减磨性能。以上研究中,部分采用了脉冲能量较大的脉冲激光器(如 Nb–YAG),有的采用了连续的光纤激光器。该类涂层的共同特点是具有熔覆区 – 结合区 – 热影响区 – 基体等多层过渡结构。为分析涂层种类带来的表面硬度梯度差别,将部分文献报道的涂层特性列入表 1[17–19,21–24,27–28,30]。
1.3 渗层与镀层
沈志超等[31] 采用无氰镀铜方法使钛合金 TC4 表面摩擦系数由 0.52降低到 0.38。田晓东等[32] 利用辉光离子渗在 TC4 钛合金表面形成MoS2–Mo 渗层,表层减磨,次表层硬化,形成硬度梯度结构。Zhao 等[33]在激光选区熔化制造的钛合金零件表面进行气体渗氮,使其纳米硬度从5.2GPa 提高到 13.3GPa,并降低了摩擦系数。此外,有些研究采用复合处理来提高钛合金耐微动磨损性能。
李瑞冬等[34] 认为喷丸+ CuNiIn 涂层可以改善微动磨损性能。刘道新等[35]采用离子渗氮后喷丸的方法,更好地提高了 TC4 合金抗微动磨损和疲劳性能。
1.4 钛合金耐磨损涂层技术展望
从以上文献分析,耐磨涂层的发展存在以下几个趋势: (1)多元、多工艺复合处理,利用制备工艺特点,制造多元或多层复合结构,在保障涂层硬度的同时,增加韧性,实现强韧化匹配; (2)加强涂层力学性能设计,通过计算仿真手段,获得外载下内应力低、结合力好且结构可靠的耐磨涂层体系。另外,工业界应在保障涂层结构分析的基础上,加强涂层的模拟服役性能试验,在实践中获得真知,加快研究结果应用。
2 、钛合金抗氧化和阻燃涂层
在室温下,钛合金表面可以形成致密的氧化膜,故具有良好的室温耐腐蚀性能。部分航空航天器使用的钛合金零件需要在中温甚至高温下使用,而该条件下形成的氧化膜是多孔的 TiO2,无法有效抵御氧原子向内扩散。另一方面,钛合金的燃点低于熔点。当航空发动机高速运动的钛合金零件因某些原因 (如变形、断裂等) 发生位移时,部件间相对运动(如转定子)高速摩擦生热可能点燃钛合金而发生钛火事故,严重危及航空航天器安全使用。因此,国内外积极开展了钛合金抗氧化涂层和阻燃涂层的研制。通过两类涂层改变钛合金表面氧化和温升机制是一个可靠方法。
2.1 抗氧化涂层
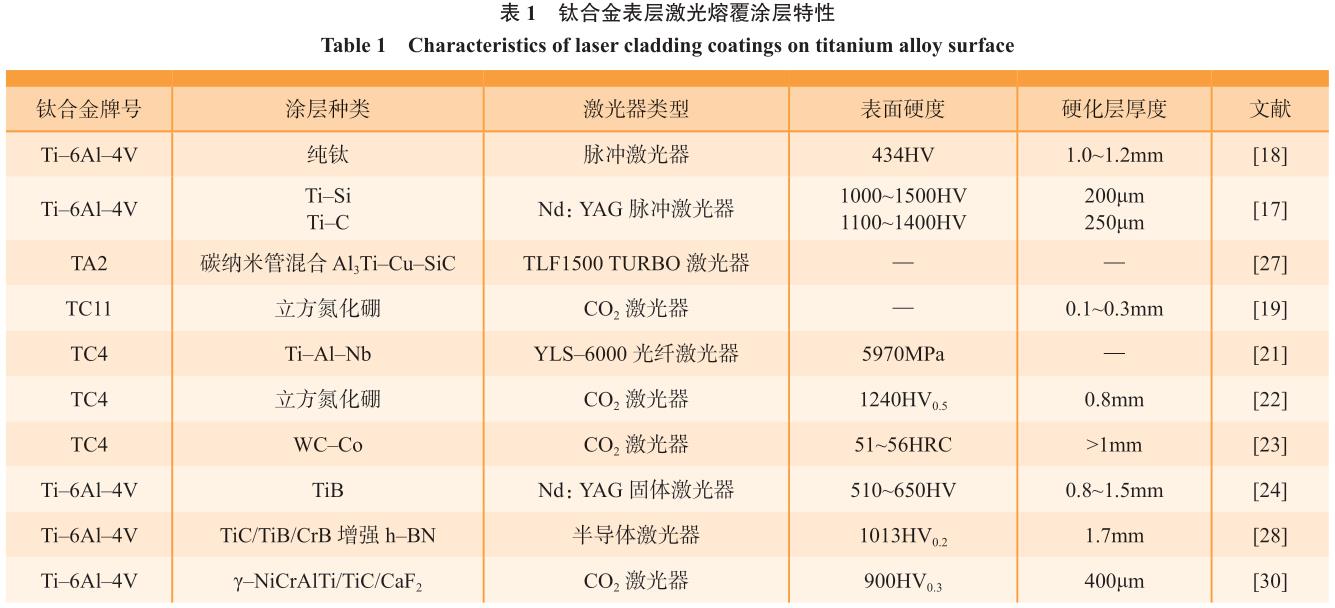
Du 等[36] 首 先 制 备 微 弧 氧 化TiO2 膜,接着采用磁控溅射方法在膜表面镀覆纯铝,最终利用阶梯式扩散热处理提高了上述两层的冶金结合;该方法制备的复合涂层(主要成分 α–Al2O3)具有良好的阻氧扩散能力,在 973~1073K 条件下显著降低了钛合金的氧化增重。Maliutina 等[37] 采用激光熔覆方式在 TiAl 合金表面制备 Ti48Al2Cr2Nb 涂层,在 700~900℃氧化过程中,其中 Nb 和 Cr 抑制了TiO2 的生长,涂层表面形成以 Al2O3为主的多层氧化膜。在工业纯钛表面,Shugurov 等[38] 采用直流磁控溅射制备了 Ti1–x–yAlxTayN 涂层,该涂层提高了 850℃氧化抗力,但无法提高950℃氧化性能,随着 Ta 元素含量增加,950℃氧化性能逐渐变差。Yin[39]的研究表明,LaB6 的适度添加可以细化激光熔覆 TiC+TiBx 涂层,提高氧化性能。Yu 等[40] 研究了不同 MoO3含量的玻璃陶瓷涂层(硼铝硅酸盐微晶玻璃)在 850~1050℃温度范围内沉积在 TA2 工业纯钛上的抗氧化行为,认为富 Mo 层起到良好抗氧化效果。Zhang[41]、汝强[42] 和陈倩[43] 等采用电弧镀或离子镀方法在钛合金表面制备含铝涂层,单晓浩等[44] 采用激光熔覆制备 Nb–Al–Ti 涂层,利用Al2O3 良好的阻氧扩散能力提高钛合金氧化抗力。除了以上的涂层技术外,表面改性方法也应用于钛合金抗氧化。Kanjer 等[45] 在纯钛表面采用WC 珠、Al2O3 珠和玻璃珠进行超声喷丸,降低了 700℃/100h 和 3000h 的氧化增重,认为喷丸样品形成的连续富氮层起到了阻氧扩散避免剥落分层的作用;He 等[46] 利用激光喷丸在Ti2AlNb 表面产生细晶层和高位错密度,提高了 720℃氧化性能。部分涂层结构如图 2 所示[36–38]。
2.2 阻燃涂层
针对钛火问题,Anderson 等[47] 提出物理气相沉积 Pt/Cu/Ni 复合涂层,王长亮等[48] 采用热喷涂铝涂层,利用涂层元素良好的导热性避免钛合金零件局部温升。Freling[49] 和 Kosing[50] 等提出采用 ZrO2 涂层用于阻燃,则利用了 ZrO2 较低的热导率。Li 等[51]采用 Ti–Cr 和 Ti–Cu 等多元金属涂层,通过涂层燃烧不敏感实现阻燃。
近年来,钛合金阻燃涂层的一个研究热点是多层结构。弥光宝等[52] 提出热喷涂方法制备 YSZ+ NiCrAl-B.e 复合涂层,实现其临界着火氧浓度提高至钛合金基体的 2.3 倍,YSZ 产生了良好的阻隔热量传输的作用。
汪瑞军[53–54]、曹江[55] 和傅斌友[56] 等提出微弧离子表面改性和热喷涂工艺技术在 TC11 基体上制备复合阻燃涂层,分别利用 Ti–Zr 非晶和 YSZ实现吸收能量和隔热,部分涂层结构如图 3 所示[52,56]。

2.3 钛合金抗氧化和阻燃涂层技术展望
从以上文献看,抗氧化涂层的主要目的是阻氧扩散,而阻燃涂层在阻氧扩散的基础上,还需要实现隔热和能量吸收。那么,对于上述涂层的发展要求一般为: (1)具有良好结合力; (2)具有包覆性、连续且具有一定厚度的阻氧扩散层 (如 α–Al2O3、TiN 等); (3)具备氧化层稳定成分(如富 Mo 层),使得氧化层形成后能够保持稳定,减少和避免剥落或分层; (4)在工艺和成分控制上,尽可能减小孔洞,避免氧原子直接快速进入基体; (5)向多元、多层结构发展,同时实现吸收能量和隔绝热量等多重目的。
3 、钛合金抗疲劳表面改性
在满足航空航天器轻量化需求的同时,钛合金零件还需要满足长寿命与高可靠性需求,这就要求钛合金零件具有良好的疲劳抗力。然而,钛合金是种典型的难加工材料,加工过程刀具可能发生粘着磨损使得表面应力复杂,加之其导热性较差导致局部温升,因此钛合金零件加工后表面完整性控制困难。工业界大量使用抗疲劳表面改性 (或表面形变强化技术,Surface mechanical treatment)来提高钛合金零件表面完整性状态,进而实现长寿命高可靠性要求。在抗疲劳表面改性中,机械喷丸(Shot peening)和激光冲击强化 (激光喷丸)(Lasershock peening or Laser peening)结 构适应性强,被业界广泛研究。部分适应特殊结构的表面强化工艺技术,如适应孔结构的冷挤压强化 (Cold expansion)和适应焊接结构的超声喷丸强化 (Ultrasonic impact treatment or Ultrasonic impact peening),也开展了系列研究。
3.1 机械喷丸
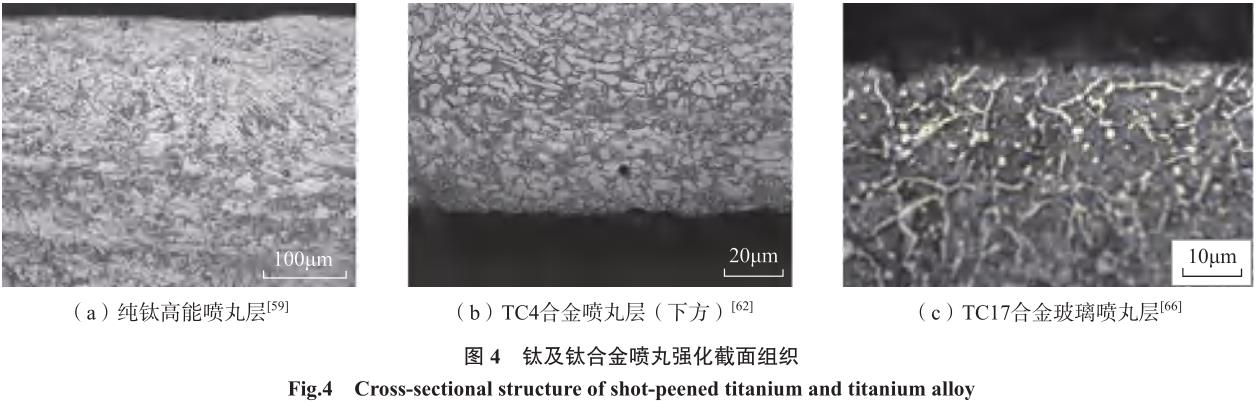
机械喷丸对表面完整性的影响主要为表面形貌、表层组织性能与残余应力。Ma 等[57–58] 利用离心式喷丸机研究了 Ti1023 钛合金大尺寸弹丸喷丸后的梯度组织。Unal 等[59] 对纯钛进行高能喷丸,分析了具有更高纳米硬度的形变超细晶组织。Wen等[60] 对 TiB+TiC 增强钛基复合材料的喷丸试验结果表明,增强相和基体界面由于喷丸挤压作用产生纳米结构和高位错密度。Yao 等[61] 对 TB6合金表面完整性的研究认为铣削 +抛光 + 喷丸 + 抛光工艺可获得最佳表面形貌、残余应力和显微硬度状态(即表面完整性状态),最大程度提高构件疲劳性能。高玉魁[62]、宋颖刚[63]等分析了喷丸对 TC4 和 TC21 合金组织结构的影响,认为表层应变硬化和宏观残余压应力是喷丸强化的重要原因。冯宝香[64] 和苏雷[65] 等分别从试验和数值模拟入手研究了喷丸对钛合金残余应力的影响。部分文献报道了喷丸强化层的金相,对比如图 4 所示[59,62,66]。
机械喷丸的主要作用是提高钛合金构件疲劳性能,在工艺应用方面,国内学者开展了大量研究。由于喷丸后表面粗糙度升高可能会影响叶片气动效率,Shi 等[67] 发现喷丸后进行光饰处理能够降低表面粗糙度,更好地提高疲劳性能。戴全春等[68]采用喷丸 + 电磁场复合处理技术,使 TC11 钛合金最大残余压应力提高了 7.7%,疲劳强度提高了 33%。王强等[69] 研究了 TC18 合金孔结构挤压强化对表面完整性和疲劳性能的影响,认为对于该合金孔结构,喷丸较冷挤压疲劳增益幅度更大,达到 3 倍以上。
张彩珍[70] 和徐鲲濠[71] 等对钛合金叶片残余应力与变形情况的研究表明,残余压应力是产生整体形变的主要原因,而采用预变形和校正方法可以解决叶片整体变形问题。邓瑛[72] 和尚建勤[73] 等认为应根据壁厚区分钛合金零件喷丸要求以实现工艺构件匹配。杜东兴等[74] 研究表明喷丸对吹砂 – 超音速火焰喷涂 TC21 合金零件的疲劳性能弱化具有弥补作用。喷丸参数对 TC4[75–77]、Ti60[78]、TC18[79] 等合金疲劳性能影响研究认为,在一定服役周期后喷丸可以进一步补充表面强化层,延长服役寿命。张少平等[66] 对比了弹丸对 TC17 合金疲劳性能的影响,认为玻璃丸喷丸疲劳增益幅度最大。
3.2 激光喷丸(激光冲击强化)
Che 等[80] 对 TC21 钛合金进行高能激光强化,强化后钛合金表面硬度提高 16% 并且粗糙度 Ra 小于 0.8μm。Wang 等[81] 对于 TC6 激光强化研究认为该工艺产生的强化层具有良好的热稳定性。
残余压应力场深度大是激光喷丸与机械喷丸的重要差别。Zhang等[82] 认为只有在较大的残余压应力作用下,疲劳裂纹扩展才会受到抑制;Sun 等[83] 从数值模拟角度分析了残余压应力对裂纹扩展的阻碍作用;李启鹏等[84] 建立了支持向量机理论的残余应力松弛模型;Shi等[85] 研究了 3mm 薄壁钛合金焊接结构激光喷丸,发现激光喷丸改变了热影响区的应力状态,产生深层残余压应力场,使疲劳强度提高了 19%。
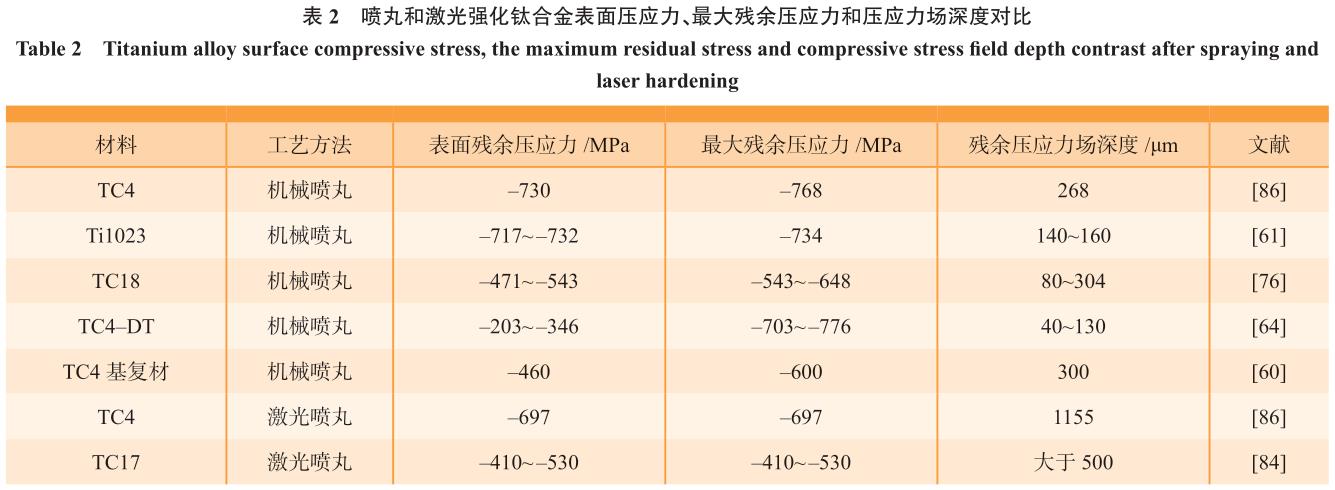
为了对比喷丸与激光强化的表面完整性特征差别,将部分文献报道的表面形貌和残余应力场特征分别列入表 2[60–61,64,76,84,86] 和图 5[86]。
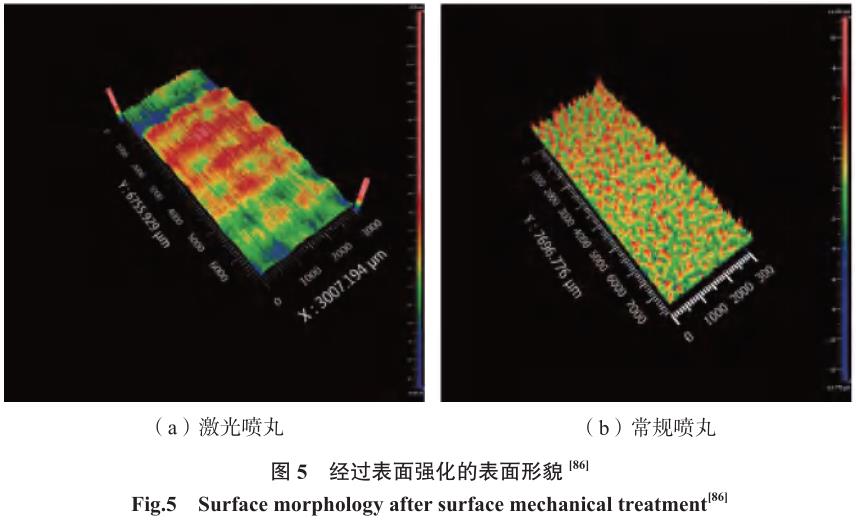
疲劳性能的增益作用是激光喷丸研究的根本目的。Luo 等[86] 对比了激光 / 机械喷丸对 TC4 钛合金 4点弯曲疲劳性能的影响,并通过对比深入解析了疲劳性能增益的原因。
Nie 等[87] 建立了综合考虑等效残余压应力和 FINDLEY 模型,在两倍误差范围内成功预测了激光喷丸 TC4钛合金试样的高周疲劳寿命。
利用激光增材制造零件是当前工业界快速制造的重要方向,在应用上,该技术产生大量内部缺陷的问题也同样引起工业界的关注。Aguado-Montero[88] 对比研究了机械、激光喷丸和机械喷丸 + 表面化学处理对增材制造 TC4 疲劳性能的影响,发现3 种情况下疲劳强度都远高于未经表面处理的参考组[89]。赖梦琪等[90]对比了锻造和增材制造 TC4 合金激光强化后的表面完整性状态,认为激光强化提高了增材制造 TC4 合金致密度,但因内部疏松的缘故使得残余压应力数值小于锻造态强化。Jiang等[91] 针对激光选区融化制造构件的超高周疲劳研究发现激光喷丸后疲劳性能更低,原因是该型疲劳试验疲劳断口起源于大深度缺陷处。
无保护(吸收)层激光喷丸(Laser shock peening without protective coating,LSPwC)和改变环境温度的激光喷丸(温激光喷丸,Warm laser peening 或 深冷激光喷丸,Cryogenic laser peening)等新方法研究丰富了激光喷丸技术树。Petroni 等[92] 对比了有无保护层激光强化钛合金微观结构和性能,发现有保护层情况下表面粗糙度更低。Pan 等[93] 对比了室温和 300℃激光喷丸后钛合金组织,特别的是一些在室温下一般不开动的孪晶(如{10 –12})可在温激光喷丸过程开动产生。Feng 等[94] 对于钛合金焊接结构温喷丸研究结果表明,疲劳极限提高了40% 以上。周建忠等[95] 采用在极低温度下进行激光喷丸,以产生数值更大的残余压应力[96]。
3.3 其他表面强化技术
为了建立良好的连接,销钉孔结构是航空器钛合金零件的重要连接方式,同时,也引入结构弱点(应力集中),导致该位置的疲劳性能薄弱,亟待加强。对于销钉孔结构,艾莹珺[97]、霍鲁斌[98]、罗学昆[99]、杨广勇[100] 和马世成[101] 等针对 TC17、TC4–DT、TB6钛合金研究了适宜的冷挤压系列方法,主要优化的工艺参数包括挤压方式、过盈量、导端角等对孔壁粗糙度、残余应力分布、疲劳性能的影响。
除冷挤压强化外,超声喷丸也是近年来钛合金表面强化研究的热点之一。Zhu 等[102–103] 认为超声喷丸使纯钛表面发生剧烈形变,可形成纳米 + 非晶的复合表层。Kumar[104]和 Mordyuk[105] 等也认为超声喷丸后将导致表面纳米化。刘德波等[106]的研究表明,降低气孔疏松等缺陷,引入强化层是超声冲击处理焊缝的主要强化作用。蔡晋等[107] 通过建立有限元模型,分析了超声强化腔体与零件待强化区域的关系,并对比了 TC4 合金喷丸和超声喷丸残余应力差别[108]。王谧等[109] 开展了超声喷丸多弹丸仿真。以上研究如能配合实际试验验证将更能够推进工艺应用。
3.4 钛合金抗疲劳表面改性技术展望
根据以上问题,认为钛合金抗疲劳表面改性技术主要有以下 3 个发展需求: (1)加强零件结构适应性。对于薄壁以及对于表面粗糙度等有特殊要求的零件,需提供专用表面强化手段或工艺参数,在控制变形和表面完整性状态的前提下实现抗疲劳强化。(2)表面改性层高能化、深层化和均匀化。目前高能深层是表面形变强化领域的普遍共识,而均匀化是工业界保障疲劳性能提高的关键,这方面容易被学术领域忽略。(3)提高成本可控性。这主要来自于表面工程技术的应用需求。在工业上,在实施表面改性技术后,如何有效表征钛合金构件的疲劳性能,探索建立表面完整性 – 试样疲劳性能 – 构件疲劳性能的内在联系,将是一个研究难点。
4、 结论
从目前西方发达国家航空航天零件使用材料的发展趋势看,比强度高、密度小的钛合金材料在很长的一段时间内仍将是航空航天使用的主要金属材料。解决该合金磨损、氧化和疲劳问题是保障钛合金零件在航空航天器可靠服役的关键。以耐磨涂层、抗氧化涂层和表面改性技术为代表的表面工程技术以其低成本、高效和不增重(或少增重)的特点,成为了解决 3 大问题的钥匙。随着我国国力逐步增强,航空航天技术将进一步快速发展,钛合金表面工程技术发展机遇巨大,同样也面临着基础研究和工艺应用带来的巨大挑战,有待广大表面工程科技工作者深入研究解决。
参 考 文 献
[1]张旺峰 , 黄旭 , 李兴无 , 等 . 钛合金的设计方法及其研究进展 [J]. 材料导报 ,2005, 19(3): 1– 4.
ZHANG Wangfeng, HUANG Xu, LI Xingwu, et al. Design method and current research development of titanium alloys[J]. Materials Review, 2005, 19(3): 1– 4.
[2] 曹春晓 . 钛合金在未来航空领域的应用前景 [J]. 国际航空 , 2006(8): 59–60.
CAO Chunxiao. Use of titanium alloys in aviation[J]. International Aviation, 2006(8): 59–60.
[3] 曹春晓 . 钛合金在大型运输机上的应用 [J]. 稀有金属快报 , 2006, 25(1): 17–21.
CAO Chunxiao. Applications of titanium alloys on large transporter[J]. Rare Metals Letters,2006, 25(1): 17–21.
[4] 曹春晓,闫渊林,黄旭 . 我国航空系统钛合金发展现状与展望 [J]. 钛工业进展 ,2002(4): 26–29.
CAO Chunxiao, YAN Yuanlin, HUANG Xu. Development status and prospects of titanium alloys in China’s aviation system[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2002(4): 26–29.
[5]蔡建明,弭光宝,高帆,等 . 航空发动机用先进高温钛合金材料技术研究与发展[J]. 材料工程 , 2016, 44(8): 1–10.
CAI Jianming, MI Guangbao, GAO Fan, et al. Research and development of some advanced high temperature titanium alloys for aero-engine[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2016,44(8): 1–10.
[6] 冯天颖 . 双层钛合金激光焊板热气胀成形极限研究 [D]. 哈尔滨 : 哈尔滨工业大学 , 2020.
FENG Tianying. Research on hot air bulging forming limit of laser welded double-layer titanium alloy sheet[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020.
[7] 曲璇中 . 航天钛合金紧固件的制造和性能 [J]. 稀有金属材料与工程 , 1992(5): 47–50.
QU Xuanzhong. Manufacturing and performance of titanium alloy fasteners for aerospace[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 1992(5): 47–50.
[8]胡愈刚,王晓平,周亮 . TC18 钛合金焊接技术在飞机起落架制造中的应用研究[J]. 航空制造技术 , 2011, 54(16): 72–74.
HU Yugang, WANG Xiaoping, ZHOU Liang,et al. Application research on TC18 titanium alloy welding technology in manufacture of aircraft landing gear[J]. Aeronautical ManufacturingTechnology, 2011, 54(16): 72–74.
[9] HONG X, FENG K, TAN Y, et al.Effects of process parameters on microstructure and wear resistance of TiN coatings deposited on TC11 titanium alloy by electrospark deposition[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 1767–1776.
[10] 曹鑫,王冠,何卫锋,等 . TC4 钛合金与多层 TiN/Ti 涂层的砂尘冲蚀损伤试验 [J].航空动力学报 , 2016, 31(9): 2218–2224.
CAO Xing, WANG Guan, HE Weifeng,et al. Sand erosion damage test on TC4 titanium alloy and TiN/Ti multilayer coating[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2016, 31(9): 2218–2224.
[11]RICHARD C, KOWANDY C,LANDOULSI J, et al. Corrosion and wear behavior of thermally sprayed nano ceramic coatings on commercially pure Titanium and Ti–13Nb–13Zr substrates[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 2010, 28: 115–123.
[12]K O S H U R O V, F O M I N A ,RODIONOV I. Composition, structure and mechanical properties of metal oxide coatings produced on titanium using plasma spraying and modified by micro-arc oxidation[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44: 12593–12599.
[13] LIU H W, XU X J, ZHU M H, et al. High temperature fretting wear behavior of WC-25Co coatings prepared by D-gun spraying on Ti–Al–Zr titanium alloy[J]. Tribology International, 2011, 44(11): 1461–1470.
[14]PAWLAK W, KUBIAK K J,WENDLER B G, et al. Wear resistant multi-layer nanocomposite WC1–X/C coating on Ti–6Tl–4V titanium alloy[J]. Tribology International, 2015,82: 400–406.
[15] 王俊,李崇桂,王一鸣,等 . 钛合金表面激光重熔 Al2O3–TiO2 涂层的试验研究 [J].应用激光 , 2013, 33(3): 219–224.
WANG Jun, LI Chonggui, WANG Yiming, et al. Experimental study of laser remelting of Al2O3–TiO2 coatings on titanium alloy[J].Applied Laser, 2013, 33(3): 219–224.
[16]MOHAZZAB B F, JALEH B,FATTAH–ALHOSSEINI A, et al. Laser surface treatment of pure titanium: microstructural analysis, wear properties, and corrosion behavior of titanium carbide coatings in hank's physiological solution[J]. Surfaces and Interfaces, 2020, 20:100597.
[17] WU Y, WANG A H, ZHANG Z, etal. Wear resistance of in situ synthesized titanium compound coatings produced by laser alloying technique[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology,2014, 258: 711–715.
[18] WANG C, LI J, WANG T, et al.Microstructure and properties of pure titanium coating on Ti–6Al–4V alloy by laser cladding[J].Surface & Coatings Technology, 2021, 416:127137.
[19]高霁,宋德阳,冯俊文 . 工艺参数对钛合金激光熔覆 CBN 涂层几何形貌的影响 [J]. 表面技术 , 2015, 44(1): 77–80.
GAO Qi, SONG Deyang, FENG Junwen.Influence of processing parameters on geometrical features of CBN coatings by laser cladding on titanium alloy surface[J]. Surface Technology,2015, 44(1): 77–80.
[20] ZHAO Y, LU M, FAN Z, et al. Laser deposition of wear-resistant titanium oxynitride/titanium composite coatings on Ti–6Al–4VAlloy[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 531:147212.
[21]戈晓岚,仲奕颖,许晓静,等 . TC4钛 合 金 表 面 激 光 合 金 化 Ti–Al–Nb 涂 层 的研究 [J]. 稀有金属材料与工程 , 2017, 46(8):2266–2270.
GE Xiaolan, ZHONG Yiying, XU Xiaojing,et al. Ti–Al–Nb coating by laser alloying on TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2017, 46(8): 2266–2270.
[22] 蒋松林 , 陈志勇 , 朱卫华 , 等 . TC4钛合金表面激光熔覆 C 与 BN 粉末原位生成复合涂层 [J]. 激光与红外 , 2010, 40(5): 459–462.
JIANG Songlin, CHEN Zhiyong, ZHU Weihua, et al. In-situ formatting composite coating by laser cladding C+BN power on TC4 alloy[J].Laser & Infrared, 2010, 40(5): 459–462.
[23]李春燕,寇生中,赵燕春,等 . 钛合金表面激光熔覆 Co–WC 复合涂层的组织及力学性能 [J]. 功能材料 . 2015, 46(7): 7025–7029.
LI Chunyan, KOU Shengzhong, ZHAO Yanchun, et al. Microstructure and mechanical property of laser cladding Co–WC composite coatings on titanium alloy surface[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2015, 46(7): 7025–7029.
[24] 林沛玲,张有凤,杨湾湾,等 . 扫描速度对激光熔覆钛合金复合涂层显微组织的影响 [J]. 热工艺技术 , 2019, 48(10): 132–135.
LIN Peiling, ZHANG Youfeng, YANG Wanwan, et al. Effect of scanning speed on microstructure of laser cladding titanium alloy composite coating[J]. Hot Working Technology,2019, 48(10): 132–135.
[25]刘丹 , 陈志勇 , 陈科培 , 等 . TC4钛合金表面激光熔覆复合涂层的组织和耐磨性 [J]. 金属热处理 , 2015, 40(3): 58–62.
LIU Dan, CHEN Zhiyong, CHEN Kepei, et al. Microstructure and wear resistance of laser clad composite coating on TC4 titanium alloy surface[J].Heat Treatment of Metals, 2015, 40(3): 58–62.
[26]刘庆辉,许晓静,戈晓岚,等 . TC4钛合金表面激光合金化 Ti–Si–C 涂层的研究[J]. 稀有金属 . 2016, 40(6): 546–551.
LIU Qinghui, XU Xiaojing, GE Xiaolan,et al. Research of laser alloying Ti–Si–C coating on TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2016, 40(6): 546–551.
[27] YE Z, LI J, LIU L, et al. Micros-tructure and wear performance enhancement of carbon nanotubes reinforced composite coatings fabricated by laser cladding on titanium alloy[J].Optics & Laser Technology, 2021, 139: 106957.
[28] 任佳,刘秀波,余鹏程,等 . 不同载荷下钛合金激光熔覆 Ni60/h–BN 自润滑耐磨复合涂层的摩擦学性能 [J]. 摩擦学学报 .2015, 35(4): 407–414.
REN Jia, LIU Xiubo, YU Pengcheng, et al.Effect of normal load on tribological properties of Ni60/h-BN self-lubricating anti-wear composite coating on Ti6Al4V alloy by laser cladding[J].Tribology, 2015, 35(4): 407-414.
[29] 相占凤,刘秀波,罗健,等 . 添加固体润滑剂 h–BN 的钛合金激光熔覆 γ–Ni 基高温耐磨复合涂层研究 [J]. 应用激光 , 2014,34(5): 383–388.
XIANG Zhanfeng, LIU Xiubo, LUO Jian, et al. Study of γ–Ni based high temperature anti-wear composite coatings with addition of h–BN solid lubricant on titanium alloy by laser cladding[J].Applied Laser. 2014, 34(5): 383–388.
[30] 罗健,刘秀波,陆小龙,等 . Ti–6Al–4V 钛合金表面激光熔覆自润滑耐磨涂层的高温稳定性 [J]. 材料热处理学报 , 2015, 36(3):194–199.
LUO Jian, LIU Xiubo, LU Xiaolong, et al.High-Temperature stability of self-lubricating wear resistant coating on Ti–6Al–4V alloy prepared by laser cladding[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2015, 36(3): 194–199.
[31]沈志超,谢发勤,吴向清,等 . TC4钛合金铜镀层的性能 [J]. 中国表面工程 .2012, 25(5): 45–49.
SHEN Zhichao, XIE Faqin, WU Xiangqing,et al. Properties of coating on TC4 titanium alloy by copper electroplating[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2012, 25(5): 45–49.
[32] 田晓东,王利捷,郑文鹏 . TC4 钛合金表面辉光离子渗 Mo 渗 S 复合处理涂层的组织和摩擦学性能 [J]. 表面技术 , 2013, 42(2):4–6.
TIAN Xiaodong, WANG Lijie, ZHENG Wenpeng. Microstructure and tribological properties of coatings prepared by glow plasma deposition Mo and S on TC4 titanium alloy[J].Surface Technology, 2013, 42(2): 4–6.
[33]ZHAO X, LIU H, LI S, et al.Combined effect of tin coating and surface texture on corrosion-wear behavior of selective laser melted Cp-titanium in simulated body fluid[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 816:152667.
[34]李瑞冬,付雪松,周文龙,等 . 喷丸强化与涂层复合表面处理改善 Ti–6Al–4V 钛合金抗微动磨损性能 [J]. 航空制造技术 , 2015,58(17): 96–99.
LI Ruidong, FU Xuesong, ZHOU Wenlong,et al. Improvement of fretting wear resistance of Ti–6Al–4V by application of shot peening and coating[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2015, 58(17): 96–99.
[35]刘道新,陈华,何家文 . 等离子渗氮与喷丸强化复合改进钛合金抗微动损伤性能 [J]. 材料热处理学报 , 2001, 22(3): 50–54.
LIU Daoxin, CHEN Hua, HE Jiawen. The effect of plasma nitriding and shot peening on the fretting damage resistance of Ti alloy[J].Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment,2001, 22(3): 50–54.
[36] DU W, ZHANG S, LUO X, et al. In-situ reaction synthesis of composite coating ontitanium alloy for improving high temperatureoxidation resistance[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 729: 970–977.
[37] MALIUTINA I N, SI-MOHAND H, SIJOBERT J, et al. Structure and oxidation behavior of γ–TiAl coating produced by laser cladding on titanium alloy[J]. Surface &
Coatings Technology, 2017, 319: 136–144.
[38]S H U G U R O V A , PA N I N A ,KASTEROV A. Effect of Ta alloying on isothermal oxidation behavior of Dc magnetron sputtered Ti1– x AlxN coatings on titanium substrate[J]. Surface &Coatings Technology, 2021, 421: 127488.
[39] YIN X, LIANG J, GAO Y, et al.Effects of LaB6 on the high-temperature oxidation behavior of TiC+TiBx reinforced titanium matrix composite coatings fabricated by laser cladding[J].Surface & Coatings Technology, 2021, 421:127445.
[40] YU F, GU D, ZHENG Y, et al.Influence of MoO3 on boron aluminosilicate glass-ceramic coating for enhancing titanium high-temperature oxidation resistance[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 2017, 729: 453–462.
[41] ZHANG M, SHEN M, XIN L, et al. High vacuum arc ion plating TiAl coatings for protecting titanium alloy against oxidation at medium high temperatures[J]. Corrosion Science,2016, 112: 36–43.
[42]汝强,胡社军,胡显奇 . 钛合金用Ti0.75Al0.25N 防护涂层的制备与抗氧化性能 [J].金属热处理 , 2010, 35(6): 88–92.
RU Qiang, HU Shejun, HU Xianqi.
Preparation and oxidation resistance of Ti0.75 Al0.25N coatings deposited on titanium alloy[J].Heat Treatment of Metals, 2010, 35(6): 88–92.
[43] 陈倩,辛丽,滕英元,等 . 氮化物涂层对钛合金抗循环氧化性能的影响 [J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报 , 2012, 32(1): 7–12.
CHEN Qian, XIN Li, TENG Yingyuan, et al.Effect of nitride coatings on the cyclic oxidation behavior of Ti6AL4V alloy[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2012, 32(1):7–12.
[44]单晓浩,王存山,于群 . 钛合金表面激光熔覆 Nb–Al–Ti 高温合金涂层组织与性能 [J]. 中国激光 , 2016, 43(8): 184–191.
SHAN Xiaohao, WANG Cunshan, YU Qun. Microstructure and property of Nb–Al– Ti high temperature alloy coatings by laser cladding on Ti alloy surfaces[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2016, 43(8): 184–191.
[45] KANJER A, OPTASANU V, DELUCAS M C M, et al. Improving the high temperature oxidation resistance of pure titanium by shot-peening treatments[J]. Surface & CoatingsTechnology, 2018, 343: 93–100.
[46]HE D, LI L, GUO W, et al.Improvement in oxidation resistance of Ti2AlNbAlloys at high temperatures by laser shock peening[J]. Corrosion Science, 2021, 184: 109364.
[47] ANDERSON G V, FUNKHOUSER M,MCDANIEL P. Coating for prevention of titanium combustion[R]. Washington: NASA, 1980.
[48] 王长亮,郭孟秋,汤智慧,等 . 一种制 备 防 钛 火 涂 层 的 方 法 : CN201110419195.X[P]. 2011–12–14.
WANG Changliang, GUO Mengqiu, TANG Zhihui, et al. Method for preparing anti-titanium-combustion coating: CN201110419195.X[P].2011–12–14.
[49] FRELING M, GUPTA D K. Coating scheme to contain molten material during gas turbine engine fires: US5921751[P]. 1999–07–13.
[50]KOSING O E, SCHARL R,SCHMUHL H J. Design improvements of the EJ200 HP compressor: from design verification engine to a future all blisk version[Z]. Louisiana USA: 2001.
[51]LI B, DING R, SHEN Y, et al.Preparation of Ti–Cr and Ti–Cu flame-retardant coatings on Ti–6Al–4V using a high-energy mechanical alloying method: A preliminary research[J]. Materials & Design, 2012, 35: 25–36.
[52]弭 光 宝,欧 阳 佩 旋,李 培 杰,等 .TC11 钛合金表面阻燃涂层的抗点燃性能及机理研究 [J]. 航空材料学报 , 2019, 39(5): 94–102.
MI Guangbao, OUYANG Peixuan, LI Peijie,et al. Ignition resistance and Mechanisms of TC11 titanium alloys with flame retardant coating[J].Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2019, 39(5):94–102.
[53]汪瑞军,马小斌,鲍曼雨 . 钛合金表面阻燃隔热复合功能涂层力学性能研究 [J].湘潭大学学报 : 自然科学版 , 2019(6): 27–34.
WANG Ruijun, MA Xiaobin, BAO Manyu.A study on mechanical properties of combustion-resistant and thermal barrier functional coating prepared on titanium alloy surface[J]. NaturalScience Journal of Xiangtan University, 2019(6):27–34.
[54] 汪瑞军,鲍曼雨,马小斌 . 一种阻燃隔热复合功能涂层性能研究 [J]. 热喷涂技术 ,2019, 11(1): 83–87.
WANG Ruijun, BAO Manyu, MA Xiaobin.A study on performance of burn-resistant and thermal barrier functional coatings[J]. Thermal Spray Technology, 2019, 11(1): 83–87.
[55] 曹江,李春福,傅斌友,等 . 微弧离子沉积阻燃涂层对 TC11 钛合金力学性能的影响 [J]. 中国表面工程 , 2014, 27(1): 51–55.
CAO Jiang, LI Chunfu, FU Binyou, et al. Effect of fire-resistant coating deposited by micro-arc ion surface modification on mechanical properties of TC11 alloy[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2014, 27(1): 51–55.
[56]傅斌友,汪瑞军,史萌,等 . 微弧离子沉积阻燃涂层及其性能 [J]. 焊接学报 ,2015, 36(6): 19–22.
FU Binyou, WANG Ruijun, SHI Meng, et al.Micro-arc ion deposition flame retardant coating and its performance[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2015, 36(6): 19–22.
[57] MA X, CHEN Z, ZHONG D, et al.Effect of rotationally accelerated shot peening on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of a metastable titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 75: 27–38.
[58]MA X, CHEN Z, LU W, et al. Continuous multi-cycle nanoindentation behavior of a gradient nanostructured metastable β titanium alloy fabricated by rotationally accelerated shot peening[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2021, 799: 140370.
[59]UNAL O, KARAOGLANLI A C, VAROL R, et al. Microstructure evolution and mechanical behavior of severe shot peened commercially pure titanium[J]. Vacuum, 2014,110: 202–206.
[60] WEN Y, WU Y, HUA L, et al. Effects of shot peening on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of surface nanocrystal layer on titanium matrix composite[J]. Materials &Design, 2021, 206: 109760.
[61] YAO C, WU D, MA L, et al. Surfaceintegrity evolution and fatigue evaluation after milling mode, shot-peening and polishing mode for TB6 titanium alloy[J]. Applied Surface Science. 2016, 387: 1257–1264.
[62]高玉魁 . 喷丸强化对 TC4 钛合金组织结构的影响 [J]. 稀有金属材料与工程 ,2010, 39(9): 1536–1539.
GAO Yukui. Effect of shot-peening on microstructure of TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010, 39(9):1536–1539.
[63]宋颖刚,高玉魁,陆峰,等 . TC21钛合金喷丸强化层微观组织结构及性能变化[J]. 航空材料学报 , 2010, 30(2): 40–44.
SONG Yinggang, GAO Yukui, LU Feng, et al. evolution of microstructure and properties of surface layer after shot peening of TC21 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2010,30(2): 40–44.
[64] 冯宝香,毛小南,杨冠军,等 . TC4–DT 钛合金喷丸残余应力场及其热松弛行为[J]. 金属热处理 , 2009, 34(4): 20–23.
FENG Baoxiang, MAO Xiaonan, YANG Guanjun, et al. Residual stress and its relaxation behavior of TCA–DT titanium alloy after shot peening[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2009, 34(4):20–23.
[65] 苏雷,龙波,邹思维,等 . 喷丸强化对 TC17 钛合金表面残余应力的影响 [J]. 航空维修与工程 , 2017(8): 79–82.
SU Lei, LONG Bo, ZOU Siwei, et al.The influence of the shot peening on TC17titanium alloy surface residual stress[J]. Aviation Maintenance & Engineering, 2017(8): 79–82.
[66] 张少平 , 谈军 , 谭靓 , 等 . 喷丸强化对 TC17 钛合金表面完整性及疲劳寿命的影响 [J]. 航空制造技术 , 2018, 61(5): 89–94.
ZHANG Shaoping, TAN Jun, TAN Liang,et al. Effect of shot peening on surface integrity and fatigue life of TC17 alloy[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 61(5): 89–94.
[67] SHI H, LIU D, PAN Y, et al. Effect of shot peening and vibration finishing on the fatigue behavior of TC17 titanium alloy at room and high temperature[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2021, 151: 106391.
[68] 戴全春,宋燕利,华林,等 . 航空发动机钛合金叶片残余应力喷丸 – 电磁场复合调控技术 [J]. 武汉理工大学学报 , 2016, 38(8):13–17.
DAI Quanchun, SONG Yanli, HUA Lin,et al. Residual stress control of titanium alloy blade of aeroengine by a shot peening combined electromagnetic treatment process[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2016, 38(8):13–17.
[69]王强,王欣,高玉魁,等 . 孔强化对TC18 钛合金疲劳寿命的影响 [J]. 材料工程 ,2011(2): 84–86.
WANG Qiang, WANG Xin, GAO Yukui, et al. Effect of strengthened hole on the fatigue life of TC18 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2011(2): 84–86.
[70] 张彩珍,杨健,魏磊,等 . 航空发动机钛合金叶片喷丸强化残余应力研究 [J]. 表面技术 , 2016, 45(4): 208–212.
ZHANG Caizhen, YANG Jian, WEI Lei,et al. Shot-peened residual stress of aeroengine titanium alloy blades[J]. Surface Technology, 2016, 45(4): 208–212.
[71]徐鲲濠,张超,高玉魁,等 . 钛合金薄壁叶片喷丸变形的研究 [J]. 表面技术 ,2016, 45(4): 69–74.
XU Kunhao, ZHANG Chao, GAO Yukui, et al. Deformation influence of shot peening on thin-wall titanium alloy blade[J]. Surface Technology.2016, 45(4): 69–74.
[72] 邓瑛,李志强,韩秀全,等 . 钛合金薄壁结构残余应力分布规律研究 [J]. 航空制造技术 , 2015, 58(17): 93–99.
DENG Ying, LI Zhiqiang, HAN Xiuquan, etal. Investigation of residual stress distribution of titanium alloy thin wall structures[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2015, 58(17): 93–99.
[73]尚建勤 . 钛合金喷丸强化影响因素分析研究 [J]. 航空制造技术 , 2013, 56(16):157–159.
SHANG Jianqin. Research on influencing factor of shot peening of titanium alloy part[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2013,56(16): 157–159.
[74] 杜东兴,刘道新,孟保利,等 . 前处理与超音速火焰喷涂金属陶瓷涂层对 TC21钛合金疲劳性能的影响 [J]. 中国科学:技术科学 , 2013, 43(5): 545–553.
DU Dongxing, LIU Daoxin, MENG Baoli,et al. Effects of pretreatment and HVOF sprayed cermet coating on fatigue properties of TC21titanium alloy[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2013, 43(5): 545–553.
[75] 王欣 , 李四清 , 孟震威 , 等 . 喷丸表面覆盖率对 TC4 钛合金表面完整性的影响[J]. 航空材料学报 , 2013, 33(3): 34–38.
WANG Xin, LI Siqing, MENG Zhenwei, et al. Influence of shot-peening coverage on surface integrity of TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2013, 33(3): 34–38.
[76]王强,乔明杰,张炜,等 . 喷丸对TC4 钛合金残余压应力场及疲劳寿命的影响[J]. 机械工程材料 , 2012, 36(12): 53–57.
WANG Qiang, QIAO Mingjie, ZHANG Wei, et al. Effect of shot peening on compressive residual stress fields and fatigue life for TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 36(12): 53–57.
[77] 王欣,许春玲,李臻熙,等 . 喷丸强度和表面覆盖率对 TC4 钛合金室温疲劳性能的影响 [J]. 材料工程 , 2020, 48(9): 142–147.
WANG Xin, XU Chunling, LI Zhenxi, et al. Effect of shot peening intensity and surface coverage on room-temperature fatigue property of TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2020, 48(9): 142–147.
[78] 王欣 , 蔡建明 , 王强 , 等 . 喷丸表面覆盖率对 Ti60 高温钛合金疲劳性能的影响[J]. 中国表面工程 , 2011, 24(5): 58–63.
WANG Xin, CAI Jianming, WANG Qiang,et al. Effect of shot peening surface coverage on the fatigue property in Ti60 high-temperature titanium alloy[J]. China Surface Engineering,2011, 24(5): 58–63.
[79] 王欣 , 高玉魁 , 王强 , 等 . 再次喷丸周期对 TC18 钛合金疲劳寿命的影响 [J].材料工程 , 2012, 40(2): 67–71.
WANG Xin, GAO Yukui, WANG Qiang, et al. Effect of Re-shot-peening on the fatigue life of TC18 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2012, 40(2): 67–71.
[80] CHE Z, YANG J, TANG N, et al.Research on laser peening of TC21 titanium alloy with high energy laser[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2014, 43(12): 2962–2965.
[81] WANG X D, LI Y H, LI Q P, et al. Property and Thermostablity Study on TC6 Titanium Alloy Nanostructure Processed by LSP[J]. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2012, 29(1): 68–76.
[82]ZHANG H, CAI Z, CHI J, et al.Fatigue crack growth in residual stress fields of laser shock peened Ti6Al4V titanium alloy[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 887:161427.
[83]SUN R, KELLER S, ZHU Y, et al. Experimental-numerical study of laser-shock-peening-induced retardation of fatigue crack propagation in Ti–17 titanium alloy[J].
International Journal of Fatigue, 2021, 145:106081.
[84]李 启 鹏 , 李 应 红 , 何 卫 锋 , 等 .TC17 钛合金激光喷丸应力场及支持向量机应力热松弛模型 [J]. 航空动力学报 , 2012, 27(2):307–311.
LI Qipeng, LI Yinghong, HE Weifeng, etal. Residual stress of laser peening processed TC17 and stress relax prediction model based on support vector machines theory[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2012, 27(2): 307–311.
[85] SHI X, FENG X, TENG J, et al.Effect of laser shock peening on microstructure and fatigue properties of thin-wall welded Ti–6A1–4V alloy[J]. Vacuum, 2021, 184: 109986.
[86] LUO X, DANG N, WANG X. The effect of laser shock peening, shot peening and their combination on the microstructure and fatigue properties of Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy[J].International Journal of Fatigue, 2021, 153:106465.
[87]NIE X, HE W, CAO Z, et al.Experimental study and fatigue life prediction on high cycle fatigue performance of laser-peened TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021, 822: 141658.
[88] AGUADO-MONTERO S, NAVARROC, VÁZQUEZ J, et al. Fatigue behaviour of PBFadditive manufactured Ti6Al4V alloy after shot and laser peening[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2022, 154: 106536.
[89]SLAWIK S, BERNARDING S,LASAGNI F, et al. Microstructural analysis ofselective laser melted Ti6Al4V modified by laser peening and shot peening for enhanced fatigue characteristics[J]. Materials Characterization,2021, 173: 110935.
[90] 赖梦琪,胡宗浩,胡永祥,等 . 增材制造钛合金激光喷丸强化表面完整性影响实验研究 [J]. 应用激光 , 2019, 39(1): 9–16.
LAI Mengqi, HU Zonghao, HU Yongxiang,et al. Effect of laser peening on surface integrity of additive manufactured titanium alloy[J].Applied Laser, 2019, 39(1): 9–16.
[91] JIANG Q, LI S, ZHOU C, et al.Effects of laser shock peening on the ultra-high cycle fatigue performance of additively manufactured Ti6Al4V alloy[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021, 144: 107391.
[92] PETRONIĆ S, ČOLIĆA K, ĐORĐEVIĆ B, et al. Effect of laser shock peening with and without protective coating on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-alloy[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020,129: 106052.
[93] PAN X, HE W, HUANG X, et al.Plastic deformation behavior of titanium alloy by warm laser shock peening: microstructure evolution and mechanical properties[J]. Surfaceand Coatings Technology, 2021, 405: 126670.
[94]FENG X, PAN X, HE W, et al.Improving high cycle fatigue performance of gas tungsten arc welded Ti6Al4V titanium alloy by warm laser shock peening[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2021, 149: 106270.
[95]周建忠,徐高峰 . 深冷激光冲击TC6 钛合金应力场及力学性能 [C]// 特种加工技术智能化与精密化——全国特种加工学术会议 . 广州 , 2017.
ZHOU Jianzhong, XU Gaofeng. Cryogenic laser shock TC6 titanium alloy stress field and mechanical properties[C]//Special Processing Technology Intelligence and Motors, The National Special Processing and Academic Conferences. Guangzhou, 2017.
[96] LI J, ZHOU J, LIU L, et al. High-cycle bending fatigue behavior of TC6 titanium alloy subjected to laser shock peening assisted by cryogenic temperature[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology. 2021, 409: 126848.
[97] 艾莹珺,王欣,宋颖刚,等 . 挤压强化对 TC17 钛合金孔结构疲劳寿命的影响 [J].航空材料学报 , 2017, 37(6): 82–87.
AI Yingjun, WANG Xin, SONG Yinggang,et al. Effect of cold expansion on fatigue lifeof hole structure of TC17 titanium alloy [J].Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2017, 37(6):82–87.
[98]霍鲁斌,曹增强,张帆,等 . TC4–DT 钛合金结构二次冷挤压强化数值模拟与实验研究 [J]. 西北工业大学学报 , 2018, 36(4):701–708.
HUO Lubin, CAO Zengqiang, ZHANG Fan, et al. Numerical and experimental study on TC4-DT titanium alloy structure after double cold expansion[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2018, 36(4): 701–708.
[99] 罗学昆,艾莹珺,王欣,等 . 二次孔挤压强化对 TB6 钛合金疲劳性能的影响 [J].航空材料学报 , 2017, 37(6): 88–94.
LUO Xuekun, AI Yingjun, WANG Xin,et al. Effect of double cold expansion of hole on fatigue property of TB6 titanium alloy[J].Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2017, 37(6):88–94.
[100]杨广勇,李萌,宋颖刚,等 . 二次孔挤压强化对 Ti1023 钛合金孔疲劳性能影响[J]. 航空材料学报 , 2016, 36(6): 68–73.
YANG Guangyong, LI Meng, SONGYinggang, et al. Effect of twice hole expansion on fatigue property of Ti1023 alloy[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2016, 36(6): 68–73.
[101]马世成,王欣,宋颖刚,等 . 孔挤压芯棒导端角对 TC17 钛合金孔结构表面完整性及疲劳性能的影响 [J]. 航空材料学报 ,2021, 41(4): 75–82.
MA Shicheng, WANG Xin, SONG Yinggang, et al. Effect of lead angle of hole expansion mandrel on surface integrity and fatigue performance of TC17 titanium alloy hole structure[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials,2021, 41(4): 75–82.
[102] ZHU L, GUAN Y, LIN J, et al. The enhanced thermal stability of the nanocrystalline-amorphous composite layer on pure titanium induced by ultrasonic shot peening[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 791: 1063–1069.
[103] ZHU L, GUAN Y, LIN J, et al. A Nanocrystalline-amorphous mixed layer obtained by ultrasonic shot peening on pure titanium at room temperature[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry.2018, 47: 68–74.
[104]KUMAR P, MAHOBIA G S,CHATTOPADHYAY K. Surface nanocrystallization of β–titanium alloy by ultrasonic shot peening[J].Materialstoday: Proceedings, 2020, 28: 486–490.
[105] MORDYUK B N, PROKOPENKOG I. Ultrasonic impact peening for the surface properties’management[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2007, 308(3–5): 855–866.
[106] 刘德波,张劲松,孔令云,等 . 超声冲击处理对 TC4 钛合金焊接试样微观组织及力学性能的影响 [J]. 铸造技术 , 2017, 38(11):2744–2746.
LIU Debo, ZHANG Jingsong, KONG Lingyun, et al. Effect of ultrasonic impact treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of TC4 welding titanium alloy specimens[J]. Foundry Technology, 2017, 38(11): 2744–2746.
[107]蔡晋,刘建邦 . 能量输入对 TC4钛合金超声喷丸力学影响的仿真研究 [J]. 表面技术 , 2019, 48(9): 140–149.
CAI Jing, LIU Jianbang. Simulation study on effect of energy input on mechanical properties of TC4 titanium alloy by ultrasonic shot peening[J].Surface Technology, 2019, 48(9): 140–149.
[108]刘辉,蔡晋,孟庆勋,等 . 超声喷丸与传统喷丸对 TC4 钛合金残余应力影响的仿真分析 [J]. 航空发动机 , 2020, 46(2): 87–92.
LIU Hui, CAI Jing, MENG Qingxun, et al.Simulation analysis of influence of ultrasonic and conventional shot peening on residual stress of TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Aero-engine, 2020,46(2): 87–92.
[109]王谧,张晓晓 . 基于多弹丸模型的 TC4 钛合金超声喷丸仿真研究 [J]. 内燃机与配件 , 2018(17): 32–34.
WANG Mi, ZHANG Xiaoxiao. Simulation research on ultrasonic shot peening of TC4 titanium alloy based on multi-shot model[J].Internal Combustion Engine & Parts, 2018(17):32–34.
相关链接














